什么是漏洞管理?
脆弱性 management is the process of identifying, 评估, 治疗, 和 reporting on security vulnerabilities in systems 和 the software 那 runs on them. 这, implemented alongside with other security tactics, is vital for organizations to prioritize possible threats 和 minimizing their "attack surface."
安全漏洞, 反过来, 指允许攻击者破坏产品及其包含的信息的技术弱点. 这个过程需要持续执行,以跟上新系统被添加到网络的步伐, 对系统所做的更改, 和 the discovery of new vulnerabilities over time.
如何自动化漏洞管理
A 漏洞管理系统 可以帮助自动化这个过程吗. 他们会使用漏洞扫描器,有时还会使用端点代理来盘点网络上的各种系统,并查找其中的漏洞.
一旦识别出漏洞, 它们带来的风险需要在不同的情况下进行评估,以便就如何最好地治疗它们做出决定. 例如, 漏洞验证可以是将漏洞的真实严重性置于上下文中的有效方法.
漏洞管理vs. 漏洞评估
一般来说,脆弱性评估是完整脆弱性管理程序的一部分. 组织可能会运行多个漏洞评估,以获得有关其漏洞管理行动计划的更多信息.
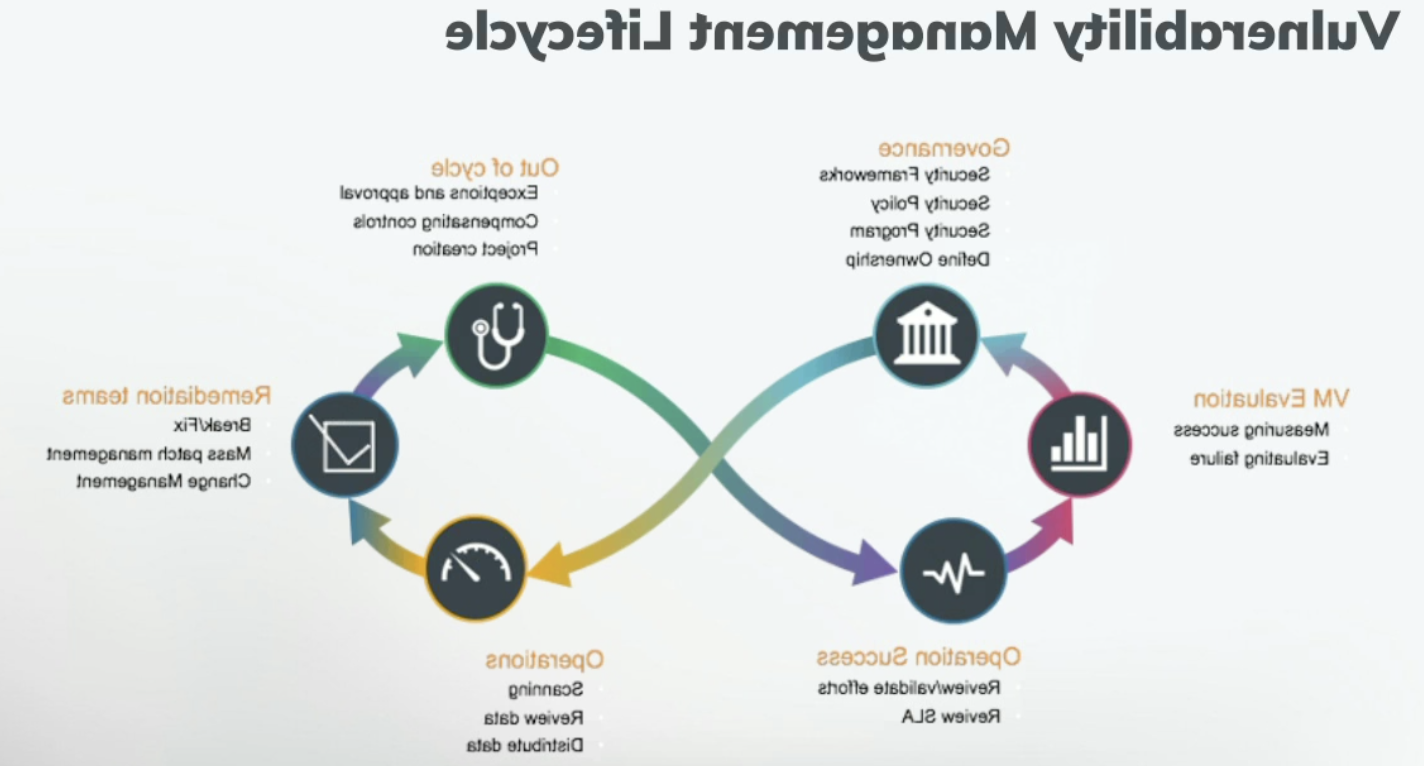
4 Steps of the 漏洞管理流程
- 执行漏洞扫描
- 评估漏洞风险
- 优先考虑 & 解决漏洞
- 持续漏洞管理
步骤1:执行漏洞扫描
At the heart of a typical vulnerability management tool is a vulnerability scanner. 扫描包括四个阶段:
- Scan network-accessible systems by pinging them or sending them TCP/UDP packets
- Identify 开放端口 和 services running on scanned systems
- If possible, remotely log in to systems to gather detailed system information
- Correlate system information with known vulnerabilities
脆弱性 scanners are able to identify a variety of systems running on a network, 比如笔记本电脑和台式电脑, 虚拟和物理服务器, 数据库, 防火墙, 开关, 打印机, 等. Identified systems are probed for different attributes: operating system, 开放端口, 安装的软件, 用户帐户, 文件系统结构, 系统配置, 和更多的.
这 information is then used to associate known vulnerabilities to scanned systems. 来执行这个关联, 漏洞扫描器将使用一个漏洞和利用数据库,其中包含一个公开已知的漏洞列表.
正确配置漏洞扫描是漏洞管理解决方案的重要组成部分. 脆弱性 scanners can sometimes disrupt the 网络 和 systems 那 they scan. If available network b和width becomes very limited during an organization’s peak hours, then vulnerability scans should be scheduled to run during off hours.
If some systems on a network become unstable or behave erratically when scanned, they might need to be excluded from vulnerability scans, or the scans may need to be fine-tuned to be less disruptive. 自适应扫描是一种基于网络变化进一步自动化和简化漏洞扫描的新方法.
例如, when a new system connects to a network for the first time, 漏洞扫描器会尽快扫描该系统,而不是等到每周或每月扫描才开始扫描整个网络.
脆弱性 scanners aren’t the only way to gather system vulnerability data anymore, though. 端点代理允许漏洞管理工具在不执行网络扫描的情况下从系统中持续收集漏洞数据.
这 helps organizations maintain up-to-date system vulnerability data whether or not, 例如, 员工s’ laptops are connected to the organization’s network or an 员工’s home network.
Regardless of how a vulnerability management solution gathers this data, 它可以用来创建报告, 指标, 以及针对不同受众的仪表板.
步骤2:评估漏洞风险
在识别漏洞之后, 需要对它们进行评估,以便适当地处理它们所构成的风险,并按照组织的标准进行处理 漏洞管理程序框架. 漏洞管理平台将为漏洞提供不同的风险评级和评分, such as Common 脆弱性 Scoring System (CVSS) scores. 这些分数有助于告诉组织他们应该首先关注哪些漏洞, 但是,任何给定的漏洞所带来的真正风险取决于这些现成的风险评级和分数之外的一些其他因素.
脆弱性风险评估因素:
- Is this vulnerability a true or false positive?
- Could someone directly exploit this vulnerability from the Internet?
- How difficult is it to exploit this vulnerability?
- Is there known, published exploit code for this vulnerability?
- What would be the impact to the business if this vulnerability were exploited?
- 是否有任何其他安全控制措施可以减少此漏洞被利用的可能性和/或影响?
- How old is the vulnerability/how long has it been on the network?
Like any security tool, vulnerability scanners aren’t perfect. Their vulnerability detection false-positive rates, while low, are still greater than zero. 执行漏洞验证 渗透测试工具 技术可以帮助排除误报,这样组织就可以将注意力集中在处理真正的漏洞上.
漏洞验证练习或全面渗透测试的结果通常会让那些认为自己足够安全或漏洞不够安全的组织大开眼界 那 有风险的.
3 .优先排序 & 解决漏洞
Once a vulnerability has been validated 和 deemed a risk, 下一步是优先考虑如何与业务或网络的原始利益相关者一起处理该漏洞. There are different ways to treat vulnerabilities, including:
- 修复: Fully fixing or patching a vulnerability so it can’t be exploited. 这 is the ideal treatment option 那 organizations strive for.
- 缓解: Lessening the likelihood 和/or impact of a vulnerability being exploited. 当一个已识别的漏洞还没有适当的修复或补丁可用时,这有时是必要的. 理想情况下,应该使用此选项为组织最终修复漏洞争取时间.
- 验收: 不采取任何措施来修复或减少漏洞被利用的可能性/影响. 这 is typically justified when a vulnerability is deemed a low risk, 并且修复漏洞的成本远远大于组织在漏洞被利用时所产生的成本.
漏洞管理解决方案 provide recommended remediation techniques for vulnerabilities. Occasionally a remediation recommendation isn’t the optimal way to remediate a vulnerability; in those cases, the right remediation approach needs to be determined by an organization’s security team, 系统所有者, 系统管理员. 补救可以像应用一个现成的软件补丁一样简单,也可以像在组织的网络中替换一组物理服务器一样复杂.
当补救活动完成时, 最好运行另一个漏洞扫描,以确认该漏洞已被完全解决.
However, not all vulnerabilities need to be fixed. 例如, 如果组织的漏洞扫描器已在其计算机上识别出Adobe Flash Player中的漏洞, 但他们完全禁止在网页浏览器和其他客户端应用程序中使用Adobe Flash Player, 然后,可以认为这些漏洞可以通过补偿控制得到充分缓解.
步骤4:持续漏洞管理
执行定期和持续的漏洞评估使组织能够随着时间的推移了解其漏洞管理程序的速度和效率. 漏洞管理工具通常具有不同的选项,用于通过各种可定制的报告和仪表板导出和可视化漏洞扫描数据.
这不仅可以帮助IT团队轻松地了解哪些补救技术可以帮助他们以最少的努力修复最多的漏洞, 或者帮助安全团队监控网络不同部分的漏洞趋势, 但它也有助于支持组织 遵从性和法规要求.
Stay Ahead with Continuous 脆弱性 Monitoring
Threats 和 attackers are constantly changing, just as organizations are constantly adding new mobile devices, 云服务, 网络, 以及应用程序对其环境的影响. With every change comes the risk 那 a new hole has been opened in your network, allowing attackers to slip in 和 walk out with your crown jewels.
每次你有了新的合作伙伴, 员工, 客户或顾客, you open up your organization to new opportunities, but you’re also exposing it to new vulnerabilities, 利用, 和威胁. 保护您的组织免受这些威胁需要一个能够跟上并适应所有这些变化的漏洞管理解决方案. Without 那, attackers will always be one step ahead.
Latest Patch Updates, Vulnerabilities, 和 Exploits
- 查看报告的最新补丁 by the Rapid7 experts on the Patch Tuesday blog
- 搜索 脆弱性 & 利用数据库 更新的风险
- 漏洞管理最新的博客文章